Optimize Testing of Electronic Control Systems in Production and Maintenance Environments with a Digital Depot
Overview
Learn about a transformative approach to unifying test equipment, data, and processes by way of the digital depot and digital production facility. Organizations that adopt a digital depot will be ideally placed to manage product lifecycle management and embrace new operational models like model-based systems engineering.
Contents
- Challenges in Testing Electronic Control Systems
- The NI Digital Depot Solution
- Optional Enhancements: MBSE, MBTE, and Digital Twins
- Industry Applications and Benefits
- Implementation Roadmap
- Looking Forward: AI-Driven Testing and Maintenance
- Conclusion
- Next Steps
The complexity of electronic control systems—such as electronic control units (ECUs) in automotive applications and line replaceable units (LRUs) in aerospace and defense—continues to escalate, challenging traditional testing methods in production facilities and depot/maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) environments. These systems demand precision, speed, and compliance with stringent standards, yet legacy approaches often fall short, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and compliance risks.
The NI digital depot and digital production facility is a transformative approach that unifies test equipment, data, and processes into a cohesive, data-driven ecosystem. Powered by NI SystemLink™ software and integrated with product lifecycle management (PLM) and operational technology (OT) applications, this solution streamlines testing, enhances reliability, and ensures traceability across the product lifecycle.
For organizations seeking to push the boundaries of efficiency and innovation, optional enhancements like model-based systems engineering (MBSE) with systems modeling language (SysML), model-based test engineering (MBTE) with Automatic Test Markup Language (ATML), and digital twins of test equipment offer advanced capabilities. These methodologies not only amplify the digital depot’s effectiveness but also lay the groundwork for future AI-driven improvements.
This white paper explores the challenges of testing electronic control systems, the NI digital depot solution, optional enhancements, and a forward-looking vision for AI integration, providing a comprehensive guide for industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
Challenges in Testing Electronic Control Systems
Testing ECUs and LRUs in production and maintenance settings presents distinct challenges:
- Production facilities—High-speed functional testing must keep pace with manufacturing throughput. However, legacy test systems often lack the flexibility to accommodate product variants or rapid design changes, leading to bottlenecks and rework.
- Depot/MRO environments—Fault diagnostics, repairs, and recertification require precise, repeatable testing aligned with regulatory standards like DO-178C (aerospace) or ISO 26262 (automotive). Disparate tools and manual processes complicate compliance and traceability. Facilities’ legacy infrastructure, fragmented systems, and manual processes delay maintenance for critical platforms compromising mission capability in both peacetime sustainment and wartime contingency operations.
- Cross-industry pain points—Unreliable test equipment, fragmented data, and poor integration between design, production, and maintenance phases hinder efficiency, root cause analysis, and decision-making. The absence of comprehensive test and measurement data from depot and production testers and real-time equipment health monitoring, both essential for predictive maintenance, operational agility, and ECU/LRU technology upgrade cycles.
These challenges underscore the need for a modern, integrated testing ecosystem capable of meeting current demands and adapting to future complexities.
The NI Digital Depot Solution
The NI digital depot and digital production facility address these challenges by creating a unified, data-driven testing environment. This solution includes the following key components:
- SystemLink Software
- Facility Health Monitoring (FHM)
- PXI-based test systems
SystemLink Software
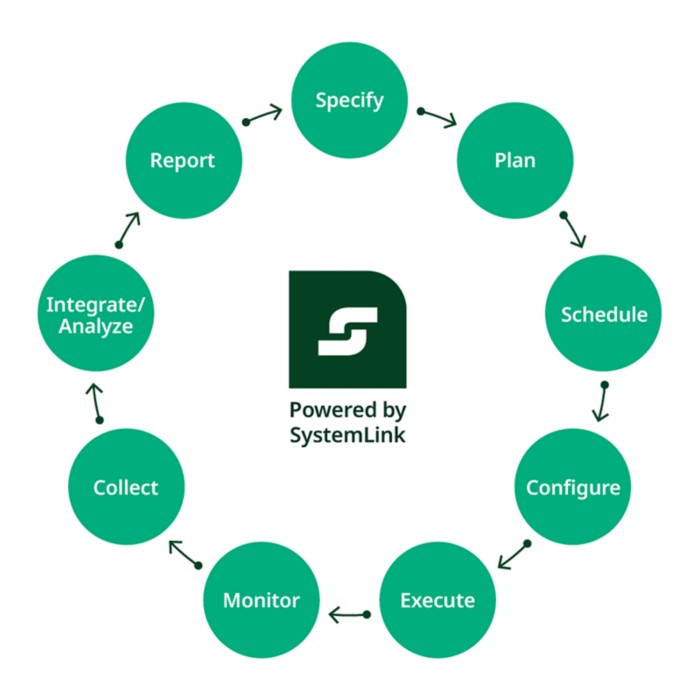
SystemLink Software centralizes test data management, automates workflows, and integrates with PLM systems, ensuring seamless data flow across the product lifecycle. The SystemLink advanced test management encompasses automated workflow orchestration, comprehensive data management, and real-time analytics with FHM proactive equipment reliability monitoring offers a transformative solution unmatched in the industry.
Figure 1: NI SystemLink software centralizes test data management, automates workflows, and integrates with PLM systems to provide a transformative solution unmatched in the industry.
Facility Health Monitoring (FHM)
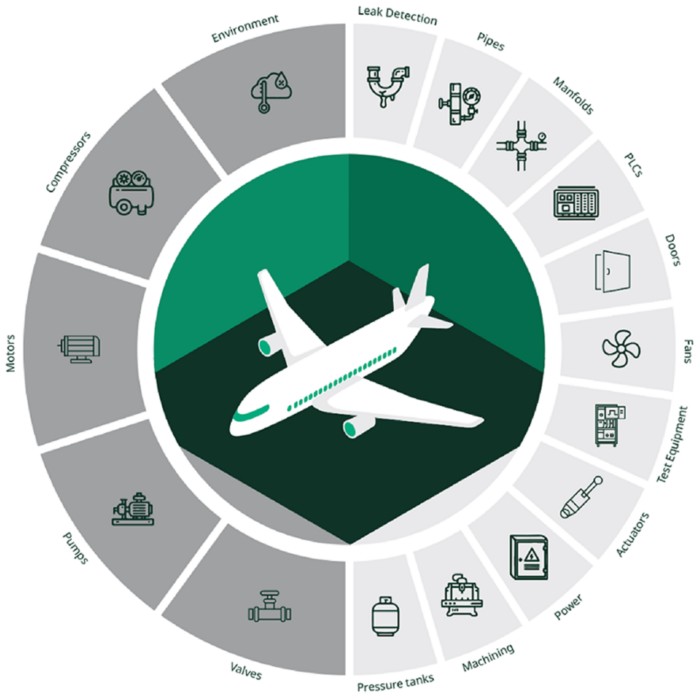
FHM is the continuous, real-time monitoring and predictive analytics for test equipment, minimizing downtime and ensuring operational readiness. FHM monitors the health of equipment that supports test, including the following examples:
Figure 2: SystemLink enables continuous test facilities’ health monitoring (FHM).
PXI-based test systems
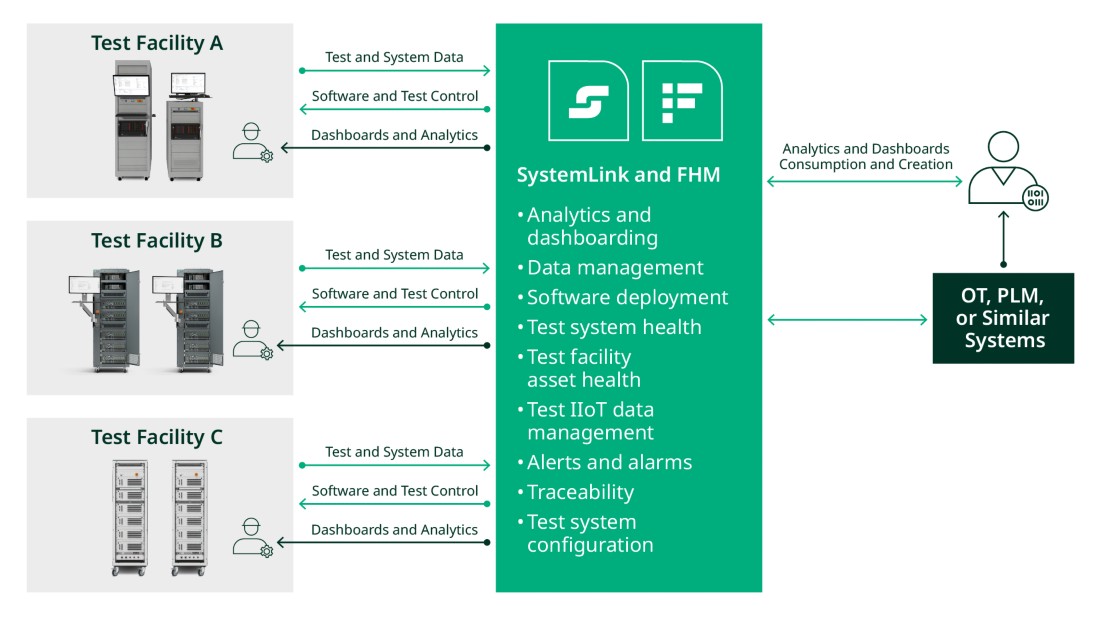
PXI systems are modular, high-performance test hardware that delivers precise, scalable testing for ECUs, LRUs, and other electronic control systems. This ecosystem establishes a digital thread—connecting production, maintenance, and design teams with real-time and historical insights. By consolidating test data and equipment management, the digital depot reduces cycle times, improves quality, and enhances visibility into testing processes.
Figure 3: The digital depot connects production, maintenance, and design teams to reduce cycle times, improve quality, and enhance visibility into testing processes.
Optional Enhancements: MBSE, MBTE, and Digital Twins
For organizations aiming to maximize the digital depot’s potential, advanced methodologies like MBSE, MBTE, and digital twins of test equipment provide optional yet powerful enhancements. These tools improve effectiveness, traceability, and compliance, offering a competitive edge in regulated industries.
Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) with SysML
MBSE leverages Systems Modeling Language (SysML) to create comprehensive models of the entire system, including test equipment, workflows, and electronic control systems. This approach enhances the digital depot in the following ways:
- Effectiveness—MBSE ensures that testing aligns with system requirements, reducing errors and rework. For example, in aerospace, MBSE models avionics systems to validate that test procedures cover all safety-critical functions.
- Traceability—By linking requirements to test outcomes within SysML models, MBSE provides an auditable trail from design to deployment—crucial for compliance with standards like DO-178C.
- Efficiency—Reusable system models streamline test development and adaptation to product variants, saving time in production environments.
Model-Based Test Engineering (MBTE) with ATML
MBTE uses both the MBSE workflows and models in a manner compatible with the Automatic Test Markup Language (ATML, IEEE 1671) to standardize test procedures and data exchange, enhancing the digital depot’s capabilities:
- Effectiveness—Standardized test definitions ensure consistency across test stations and product variants. In automotive production, MBTE enables rapid reconfiguration of ECU tests, cutting development time.
- Traceability—ATML structures test data in a machine-readable format, creating a clear record of test conditions, results, and equipment configurations—ideal for audits and root cause analysis.
- Reusability—Predefined ATML test templates reduce redundancy, enabling faster deployment of tests in both production and depot settings.
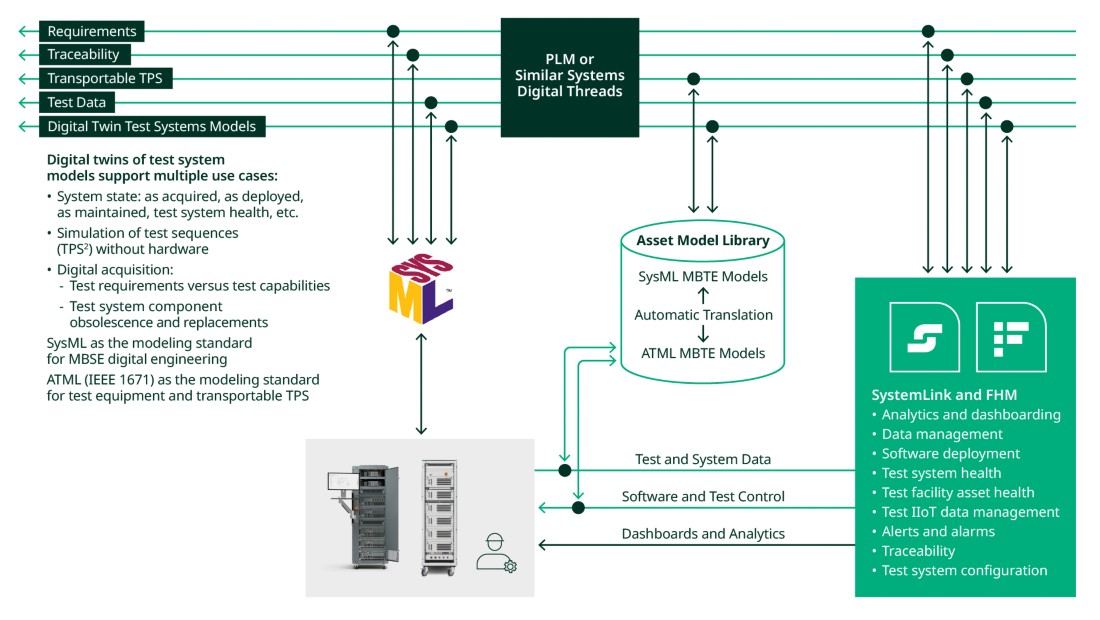
Figure 4: MBSE and MBTE workflows and tools can be integrated through digital threads with digital depots and FHM solutions built with SystemLink.
Digital Twins of Test Equipment
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical test equipment, integrated into the digital depot to optimize performance:
- Effectiveness—By simulating test scenarios, digital twins identify inefficiencies and optimize test sequences before execution. An aerospace depot might use a digital twin to develop test sequences independent of the test system, refine LRU test protocols, improving fault detection rates.
- Traceability—Digital twins log equipment performance and maintenance history, ensuring compliance with operational standards and facilitating audits.
- Predictive maintenance—Real-time data from digital twins, combined with SystemLink’s FHM, enables prediction of equipment failures and reduces downtime.
Together, these enhancements elevate the digital depot’s precision, adaptability, and readiness for complex testing demands.
Industry Applications and Benefits
The digital depot, with its optional enhancements, delivers tangible benefits across industries:
Aerospace and Defense
- Compliance—MBSE with MBTE can help ensure tests meet DO-178C requirements (for example) with full traceability from requirements to results.
- Uptime—Digital twins predict test equipment maintenance needs, reducing downtime in depot operations.
- Quality—Integrated data from SystemLink improves fault diagnostics for LRUs, enhancing reliability.
Automotive
- Speed—MBSE with MBTE and SystemLink streamline ECU test development, cutting cycle times in production facilities.
- Flexibility—MBSE with MBTE models adapt tests to new vehicle variants, maintaining throughput despite design changes.
- Efficiency—Centralized data reduces redundant testing, optimizing resource use.
Manufacturing
- Reliability—FHM helps ensures test stations remain operational, minimizing disruptions.
- Scalability—PXI systems and digital twins support testing of diverse electronic control systems, from industrial IoT devices to consumer electronics.
These examples highlight how the digital depot—enhanced by MBSE, MBTE, and digital twins—drives operational excellence.
Implementation Roadmap
Deploying the digital depot follows a structured, phased approach:
- Assessment—Evaluate current testing processes, equipment, and data gaps.
- Core deployment—Install SystemLink, PXI-based test systems, and FHM to establish the digital thread.
- Enhancement integration—Incorporate MBSE (SysML), MBTE (ATML), and digital twins as needed, aligning with industry-specific or program requirements.
- Optimization—Leverage data insights to refine workflows and improve test efficiency.
This roadmap ensures a smooth transition to a fully integrated testing ecosystem.
Looking Forward: AI-Driven Testing and Maintenance
The digital depot’s robust foundation—enriched by MBSE, MBTE, and digital twins—sets the stage for AI to revolutionize testing and equipment management. The data-rich environment created by SystemLink, PLM integration, and standardized methodologies with standardized data provides the high-quality inputs AI requires for impactful insights.
AI for Testing Effectiveness
AI can analyze historical test data from the digital depot to meet the following goals:
- Predict failures—Identify patterns that precede defects, enabling proactive test adjustments. For instance, in automotive ECU testing, AI could reduce failure rates by flagging at-risk units early.
- Optimize test sequences—Eliminate redundant tests and prioritize critical checks, shortening test cycles without compromising quality.
AI for Testing Efficiency
By processing real-time and historical data, AI enhances operational efficiency in the following ways:
- Automated test development —AI suggests test parameters based on MBSE models and past results, accelerating MBTE implementation.
- Resource allocation—AI balances test station workloads, ensuring optimal use of equipment and personnel.
AI for Test Equipment Utilization
AI maximizes the value of test assets in the following ways:
- Predictive maintenance—Building on digital twins, AI forecasts equipment failures with greater accuracy, scheduling maintenance to avoid disruptions.
- Dynamic scheduling—AI optimizes test equipment usage across production and depot environments, reducing idle time and bottlenecks.
Foundation for AI Success
The digital depot’s structured data (using ATML), system models (using SysML compatible with ATML), and real-time monitoring (using digital twins) create an ideal environment for AI. As AI adoption grows, organizations can expect significant gains in testing speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness, positioning them as leaders in their industries.
Conclusion
The NI digital depot and digital production facility transform the testing of electronic control systems, addressing the complexities of production and maintenance environments. Optional enhancements—MBSE with SysML, MBTE with ATML, and digital twins of test equipment—elevate this solution by enhancing effectiveness, traceability, and compliance. These advancements not only solve today’s challenges but also build a foundation for AI-driven innovation, promising unprecedented improvements in testing effectiveness, efficiency, and equipment utilization. With NI’s expertise and cutting-edge tools, organizations can achieve operational excellence and prepare for the future of testing.